Introducing the cell membrane & tonicity worksheet, an engaging and informative resource that delves into the fascinating world of cell biology. This worksheet explores the structure and function of the cell membrane, the concept of tonicity, and its impact on cells.
Prepare to embark on a journey of scientific discovery!
The cell membrane, the gatekeeper of the cell, plays a crucial role in maintaining cell integrity and regulating the exchange of substances. Tonicity, on the other hand, refers to the relative concentration of solutes in a solution compared to the cell, and it significantly influences cell shape and volume.
This worksheet will provide a comprehensive understanding of these fundamental concepts through interactive experiments and thought-provoking activities.
Cell Membrane Structure and Function
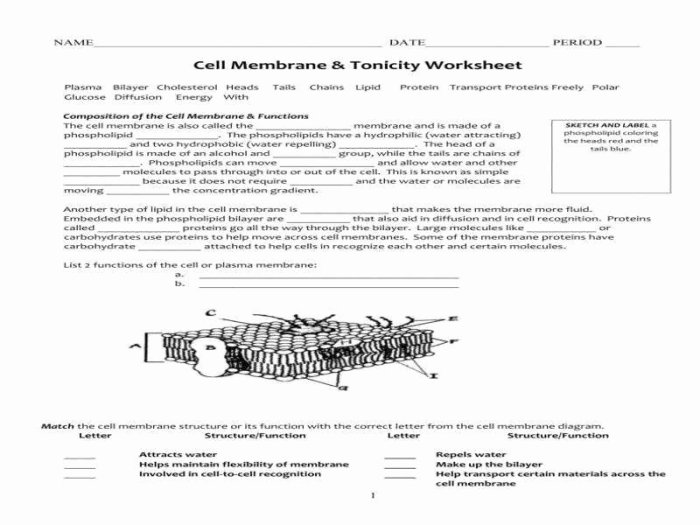
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds and protects the cell. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer, a double layer of phospholipids, which are molecules with a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail. The hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids face each other, forming a nonpolar interior that acts as a barrier to the passage of water-soluble molecules.
The hydrophilic heads of the phospholipids face outward, interacting with the aqueous environment both inside and outside the cell.
The cell membrane is not simply a passive barrier. It also contains a variety of proteins that play an active role in the transport of molecules across the membrane, the recognition of other cells, and the transmission of signals. The cell membrane is essential for maintaining cell integrity and regulating substance exchange.
Tonicity and its Effect on Cells, Cell membrane & tonicity worksheet
Tonicity is a measure of the osmotic pressure of a solution, or its ability to cause water to move across a semipermeable membrane. Tonicity is important in biology because it affects the shape and volume of cells. There are three types of tonicity: isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic.
- Isotonic solutionshave the same osmotic pressure as the cell. In an isotonic solution, water moves equally in and out of the cell, and the cell maintains its normal shape and volume.
- Hypotonic solutionshave a lower osmotic pressure than the cell. In a hypotonic solution, water moves into the cell, causing it to swell and burst.
- Hypertonic solutionshave a higher osmotic pressure than the cell. In a hypertonic solution, water moves out of the cell, causing it to shrink and become crenated.
FAQ: Cell Membrane & Tonicity Worksheet
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell, maintaining cell integrity and homeostasis.
How does tonicity affect cell shape?
Tonicity can cause cells to swell (hypotonic solution), shrink (hypertonic solution), or remain unchanged (isotonic solution).
What are some applications of tonicity in biotechnology?
Tonicity is utilized in cell culture, drug delivery, and cryopreservation to maintain cell viability and function.

